Occipital alpha rhythm neurofeedback¶
The simplest example of an experiment using NFB Lab is alpha rhythm training in the neurofeedback paradigm. As a feedback signal, the derived signal was used with the following settings: the spatial filter is determined during the experiment, the frequency filtering band is 9-11 Hz, the envelope detector is a sequence of complex demodulation, the 4th-order Butterworth filter is used in the specified band, and smoothing by the Savitzky–Golay filter of the 2nd order with a window width of 151 samples. At a sampling rate of 250 Hz, these settings, due to the causality of the used filters, introduce a delay of 131 ms. When evaluating the envelope versus non-causal filtering, the correlation of the reconstructed envelope versus the envelope obtained by the Hilbert transform is 0.7. The experiment is divided into 19 blocks
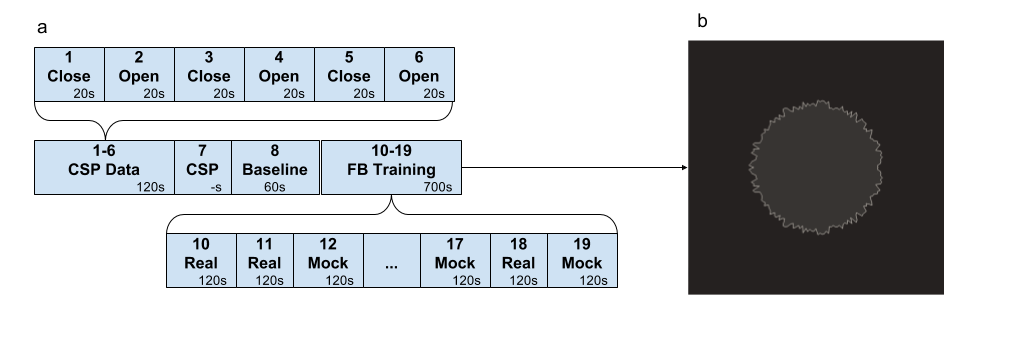
Fig. 1. Experiment sequence (a) and feedback stimulus (b).
In the first part of the experiment (blocks 1-6 “Open” and “Close”) EEG data are recorded in states with eyes open and closed, respectively. Further, in block 7 (“CSP”), using the module “Filter settings by collected data”, a spatial filter corresponding to the alpha rhythm is selected from the functional samples obtained in blocks 1-6. For this, CSP analysis of “Open” vs. “Close” blocks is used. The use of CSP is motivated by the assumption that the source generating the alpha rhythm works in a synchronous mode with the eyes closed and de-synchronizes when the eyes are open.
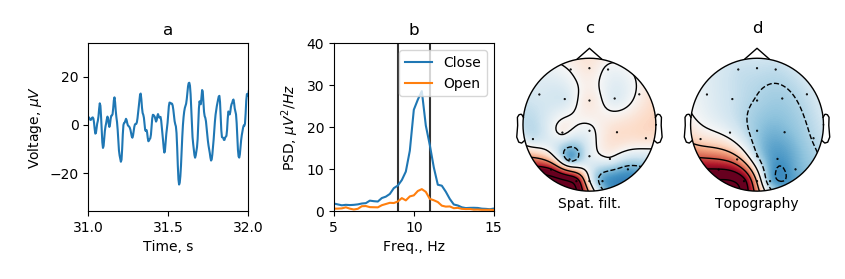
Fig. 2. Properties of the feedback signal.
Figure 2 shows the properties of the selected CSP component, namely, a portion of the time series with a pronounced alpha spindle (a), the spectrum of the component in two states Open and Close (b), a spatial filter (c), and topography (d). Next, the resting state (Baseline) is recorded to calculate the z-score of signal statistics (mean and standard deviation). These statistics are needed to correctly display the reinforcing stimulus (b) in the future. This stimulus is an inflating circle and assumes that the mean of the selected signal is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. The roughness of the border of the circle is inversely proportional to the input signal. After that, training is carried out in the NFB paradigm: 10 sessions of 2 minutes without a break, among which half of the sessions are based on the presentation of a false (Mock) feedback (not corresponding to the current activity of the brain), and the second half is real feedback (Real).
The experiment design is available at the link (https://github.com/nikolaims/nfb/blob/master/tests/designs/alpha_nfb_settings.xml).